Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide Silicon carbide is a non metal heating element in the most widely used. It is based on the green a-SiC as the main raw material, through the extrusion of green, in the high temperature (2000 degrees Celsius above) recrystall
Abstract
- Promulgator: :industrial furnace
- Send date:2016-08-14 09:58
Keywords:Silicon carbide, silicon carbon rod, SiC, silicon carbon tube
Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide is a non metal heating element in the most widely used. It is based on the green a-SiC as the main raw material, through the extrusion of green, in the high temperature (2000 degrees Celsius above) recrystallization. Silicon carbide is generally hollow rod at both ends of the bold, when made of tubular, called silicon carbon tube.
Silicon carbide by central heating and non heating in the cold end, the cold ends in bold is through increased end of basal area to reduce end resistance. In order to increase the effective heating surface area and reduce the quality, and reduce the energy consumption required by the heating body, the heating part of the middle part is usually made into a hollow part. In recent years, in order to make effective use of energy, and adapt to the new structure of industrial furnace, developed many different shapes of silicon carbide.

Silicon carbide
Silicon carbide surface load and electrical resistivity were electrothermal alloy is much higher than, temperature coefficient of resistance in 20 to 900 DEG C is negative, about 900 DEG C curve changed from negative, this feature can prevent the silicon carbide rod due to surge voltage and burned.
Physical properties of silicon carbide rod component texture hard and brittle and resistant to sudden cold and hot, high temperature is not easy to deform, and other physical properties are as follows: density: 3.2 g / cm 3 'Mohs hardness: 9.5' than the heat: 0.17 thousand card / kg and degree 'thermal conductivity: 20 kcal / m, H. - degree' coefficient of linear expansion: 5 x 10-6 (M / C).
Silicon carbide heating elements, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and wear resistance of good, under the condition of high temperature quench heat better, high temperature has sufficient mechanical strength. The silicon carbide does not react with sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, but can occur following reaction with SiC on the surface of Si02:
H2SiF6+2H20 - Si02+6HF
So that the antioxidant protective film damage, make the life reduction of silicon carbide. Alkali and alkaline earth metals, silicates and boron compounds have a corrosive effect on rod under high temperature.
Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide on its role is slow, at about 650 degrees Celsius in the air began to oxidation, high temperature oxidation. Strong oxidation reaction occurs with water vapor contact
.
Sic+2O2, Sio2+CO2, Sic+4H2O = Sio2+4H2+CO2
Silicon carbide and hydrogen contact will become brittle. Nitrogen, ammonia, chlorine and other high temperature have a different degree of decomposition of silicon carbide, so that the resistance is rapidly increasing. In particular, chlorine, at about 600 degrees Celsius can make the slow decomposition of silicon carbide, at 1200 C, there will be completely broken down.
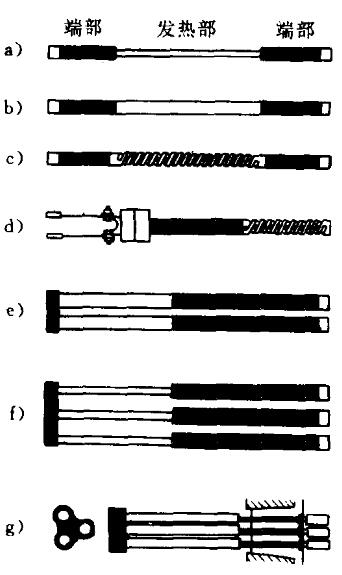
The type of silicon carbide
a) B b)equal diameter rod type C) spiral U type D type E type U (f) W type (3 phase) g) special 3 phase type
More Silicon carbide:http://www.industrial-furnace.com/furnaceaccessories/Electric_Heating_Elements/silicon_carbide.html



