Quenching defects,causes and prevention
Keywords:Quenching,decarburization,deformation,crack,overheating,hardness,soft spots,cracking,heat treatment,oxidation,grain
Quenching defects, causes and prevention
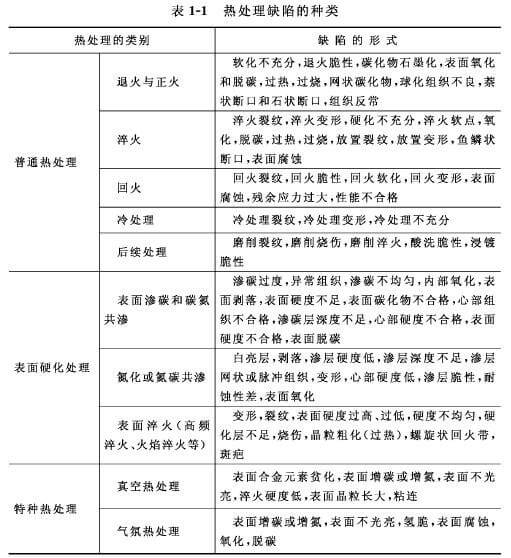
Common defects in quenching include oxidation, decarburization, deformation, cracking, overheating, over-burning, insufficient hardness, soft spots, soft spots, etc., among which oxidation, decarburization, overheating, deformation and cracking are the most serious.
Quenching, decarburization, deformation, crack, overheating, overburning, hardness, soft spots, soft spots, cracking, heat treatment, oxidation, grain
The main reason for the oxidation and decarburization phenomenon is that the heating medium contains oxidizing substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor. When heated, they chemically react with iron or carbon on the surface of the part to form iron oxide scale or carbon on the surface. Burning and becoming carbon-poor.
How to prevent the generation of oxidation and decarburization? In box-type electric furnaces and well-type electric furnaces, there are protective gases, but also by adding kerosene, methanol, or ammonia, nitrogen and other gases to protect them; The solution is to put some firewood and generate gas such as co to protect it. At present, coating a surface with a protective agent in the form of a coating can also effectively prevent oxidation and decarburization of the part. In the salt bath furnace, silica gel is generally used for deoxidation to obtain good effects.
Insufficient hardness is often caused by insufficient heating, short holding time or slow cooling. High carbon steel heating temperatures can also cause insufficient hardness.
Therefore, it is possible to prevent such defects by using a reasonable heating specification and a correct operation method (such as leaving a certain gap between the parts during heating and stirring during cooling).
The coarse grains of the structure are mainly formed due to the excessive heating temperature. Only by strictly controlling the temperature and doing the first heat treatment can we effectively prevent overheating.
Deformation and cracking are the most serious defects of heat treatment, and the root cause of such defects is excessive internal stress. When the internal stress is greater than the yield limit of the material, the part will be plastically deformed; when the internal stress exceeds the strength limit, the part will crack. Specifically, the shape of the part is asymmetrical, the thickness of the section is uneven, the original structure is poor, the heating and cooling is improper, and the shape of the sharp corners causes the deformation and cracking of the part. Only by taking targeted measures, especially the selection of reasonable process parameters, can effectively prevent such defects.
More Quenching defects,causes and prevention:http://www.industrial-furnace.com/articles/quenching_defect.html
Pre:Advantages of the inverted trolley furnace ,Next:None





